Install rsyslog using yum install rsyslog rsyslog-gnutls.
If you have not already done so, generate a self-signed CA certificate and private key. See the notes on certificates .
Generate a CA-signed certificate and private key for the log server and each client. See the notes on certificates .
On the log server and each client, place the CA certificate at /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchor/, and run update-ca-trust.
Install each host’s certificate and private key at /etc/pki/rsyslog/. Ensure that you use chmod to remove the read permissions from the private key.
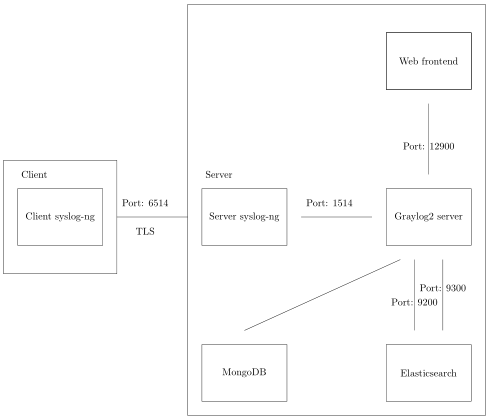
On the server, ensure a large disk exists at /mnt/sda1 and place the following in /etc/rsyslog.conf, replacing example.com and logserver.example.com:
$ ModLoad imuxsock
$ ModLoad imtcp
$ DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
$ DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile / etc / pki / ca - trust / source / anchors / example . com . pem
$ DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile / etc / pki / rsyslog / logserver . example . com . pem
$ DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile / etc / pki / rsyslog / logserver . example . com . key
$ InputTCPServerStreamDriverAuthMode x509 / name
$ InputTCPServerStreamDriverPermittedPeer *. example . com
$ InputTCPServerStreamDriverMode 1
$ InputTCPServerRun 6514
*. info ; mail . none ; authpriv . none ; cron . none / var / log / messages
authpriv .* / var / log / secure
mail .* -/ var / log / maillog
cron .* / var / log / cron
local7 .* / var / log / boot . log
On each client, place the following in /etc/rsyslog.conf, replacing example.com, logserver.example.com, and logclient.example.com:
$ModLoad imuxsock
$ModLoad imjournal
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/example.com.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile /etc/pki/rsyslog/logclient.example.com.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile /etc/pki/rsyslog/logclient.example.com.key
$ActionSendStreamDriverAuthMode x509/name
$ActionSendStreamDriverPermittedPeer logserver.example.com
$ActionSendStreamDriverMode 1
*.* @@(o)logserver.example.com:6514;RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23Format
On each host, run systemctl enable rsyslog and systemctl restart rsyslog.
Permit rsyslog traffic through the server’s firewall:
Place the following in /etc/firewalld/services/syslog.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<service>
<short>Syslog</short>
<description>Remote syslog</description>
<port protocol="tcp" port="6514"/>
</service>
Run firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service rsyslog.
You can troubleshoot rsyslog by running it manually: rsyslogd -nd.
The EPEL repository provides the syslog-ng package for CentOS or RHEL: rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm.
Remove rsyslog using yum remove rsyslog.
Install syslog-ng using yum install syslog-ng.
If you have not already done so, generate a self-signed CA certificate and private key. See the notes on certificates .
Generate a CA-signed certificate and private key for the log server and each client. See the notes on certificates .
On the log server and each client, place the CA certificate at /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/, and run update-ca-trust.
Calculate the hash of the CA certificate’s common name with openssl x509 -noout -hash -in example.com.pem.
Within /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/, create a symbolic link from hash.0 to example.com.pem, where hash is the output from the previous step.
Install each host’s certificate and private key at /etc/pki/syslog-ng/. Ensure that you use chmod to remove the read permissions from the private key.
On the server, place the following in /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf, replacing example.com and logserver.example.com:
@ version : 3.5
@ include "scl.conf"
options {
flush_lines ( 0 );
time_reopen ( 10 );
log_fifo_size ( 1000 );
chain_hostnames ( off );
use_dns ( no );
use_fqdn ( no );
create_dirs ( no );
keep_hostname ( yes );
};
source s_sys {
system ();
internal ();
};
source s_net {
syslog ( ip ( 0.0 . 0.0 ) port ( 6514 )
transport ( "tls" )
tls ( ca - dir ( "/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors" )
cert - file ( "/etc/pki/rsyslog/logserver.example.com.pem" )
key - file ( "/etc/pki/rsyslog/logserver.example.com.key" )
)
);
};
destination d_cons { file ( "/dev/console" ); };
destination d_mesg { file ( "/var/log/messages" ); };
destination d_auth { file ( "/var/log/secure" ); };
destination d_mail { file ( "/var/log/maillog" flush_lines ( 10 )); };
destination d_spol { file ( "/var/log/spooler" ); };
destination d_boot { file ( "/var/log/boot.log" ); };
destination d_cron { file ( "/var/log/cron" ); };
destination d_kern { file ( "/var/log/kern" ); };
destination d_mlal { usertty ( "*" ); };
filter f_kernel { facility ( kern ); };
filter f_default { level ( info .. emerg ) and
not ( facility ( mail )
or facility ( authpriv )
or facility ( cron )); };
filter f_auth { facility ( authpriv ); };
filter f_mail { facility ( mail ); };
filter f_emergency { level ( emerg ); };
filter f_news { facility ( uucp ) or
( facility ( news )
and level ( crit .. emerg )); };
filter f_boot { facility ( local7 ); };
filter f_cron { facility ( cron ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_kernel ); destination ( d_kern ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_default ); destination ( d_mesg ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_auth ); destination ( d_auth ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_mail ); destination ( d_mail ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_emergency ); destination ( d_mlal ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_news ); destination ( d_spol ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_boot ); destination ( d_boot ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); source ( s_net ); filter ( f_cron ); destination ( d_cron ); };
@ include "/etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/*.conf"
On each client, place the following in /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf, replacing example.com, logserver.example.com, and logclient.example.com:
@ version : 3.5
@ include "scl.conf"
options {
flush_lines ( 0 );
time_reopen ( 10 );
log_fifo_size ( 1000 );
chain_hostnames ( off );
use_dns ( no );
use_fqdn ( no );
create_dirs ( no );
keep_hostname ( yes );
};
source s_sys {
system ();
internal ();
};
destination d_cons { file ( "/dev/console" ); };
destination d_mesg { file ( "/var/log/messages" ); };
destination d_auth { file ( "/var/log/secure" ); };
destination d_mail { file ( "/var/log/maillog" flush_lines ( 10 )); };
destination d_spol { file ( "/var/log/spooler" ); };
destination d_boot { file ( "/var/log/boot.log" ); };
destination d_cron { file ( "/var/log/cron" ); };
destination d_kern { file ( "/var/log/kern" ); };
destination d_mlal { usertty ( "*" ); };
destination d_net {
syslog ( "logserver.example.com" port ( 6514 )
transport ( "tls" )
tls ( ca - dir ( "/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors" )
cert - file ( "/etc/pki/syslog-ng/logclient.example.com.cert" )
key - file ( "/etc/pki/syslog-ng/logclient.example.com.key" )
)
);
};
filter f_kernel { facility ( kern ); };
filter f_default { level ( info .. emerg ) and
not ( facility ( mail )
or facility ( authpriv )
or facility ( cron )); };
filter f_auth { facility ( authpriv ); };
filter f_mail { facility ( mail ); };
filter f_emergency { level ( emerg ); };
filter f_news { facility ( uucp ) or
( facility ( news )
and level ( crit .. emerg )); };
filter f_boot { facility ( local7 ); };
filter f_cron { facility ( cron ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_kernel ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_kern ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_default ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_mesg ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_auth ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_auth ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_mail ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_mail ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_emergency ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_mlal ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_news ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_spol ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_boot ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_boot ); };
log { source ( s_sys ); filter ( f_cron ); destination ( d_net ); destination ( d_cron ); };
@ include "/etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/*.conf"
On each host, run systemctl enable syslog-ng and systemctl restart syslog-ng.
Permit syslog-ng traffic through the server’s firewall:
Place the following in /etc/firewalld/services/syslog.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<service>
<short>Syslog</short>
<description>Remote syslog</description>
<port protocol="tcp" port="6514"/>
</service>
Run firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service syslog.
Install Nxlog community edition on the Windows client.
Install the host’s TLS key material at C:\Program Files (x86)\nxlog\cert.
Configure Nxlog by writing to C:\Program Files (x86)\nxlog\conf\nxlog.conf:
define ROOT C:\Program Files (x86)\nxlog
ModuleDir %ROOT%\modules
CacheDir %ROOT%\data
Pidfile %ROOT%\data\nxlog.pid
SpoolDir %ROOT%\data
LogFile %ROOT%\data\nxlog.log
<Extension syslog>
Module xm_syslog
</Extension>
<Input in>
Module im_msvistalog
</Input>
<Output out>
Module om_ssl
Host logserver.example.com
Port 6514
CAFile %ROOT%\cert\ca.pem
CertFile %ROOT%\cert\logserver.example.com.pem
CertKeyFile %ROOT%\cert\logserver.example.com.key
AllowUntrusted FALSE
Exec to_syslog_ietf();
OutputType Syslog_TLS
</Output>
<Route 1>
Path in => out
</Route>
Restart the Nxlog service.
Test connectivity by generating a log message on the Windows hosts using: eventcreate /ID 1 /L APPLICATION /T INFORMATION /SO MYEVENTSOURCE /D "Hello, world!".
Stop the default logging service using /etc/init.d/log stop.
Remove the default logging service using opkg remove logd.
Remove the existing log with rm /var/log/messages.
Install syslog-ng using opkg install syslog-ng.
On the server, place the following in /etc/syslog-ng.conf:
@ version : 3.8
options {
chain_hostnames ( no );
create_dirs ( yes );
flush_lines ( 0 );
keep_hostname ( yes );
log_fifo_size ( 256 );
log_msg_size ( 1024 );
stats_freq ( 0 );
flush_lines ( 0 );
use_fqdn ( no );
};
source sys {
internal ();
unix - dgram ( "/dev/log" );
};
source net {
syslog ( ip ( 0.0 . 0.0 ) port ( 6514 )
max - connections ( 50 )
transport ( "tls" )
tls ( ca - dir ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/anchors" )
cert - file ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/logserver.example.com.cert" )
key - file ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/logserver.example.com.key" )
)
);
};
source kernel {
file ( "/proc/kmsg" program_override ( "kernel" ));
};
destination messages {
file ( "/mnt/sda1/var/log/messages" );
};
log {
source ( sys );
source ( net );
source ( kernel );
destination ( messages );
};
On each client, place the following in /etc/syslog-ng.conf (replace SERVER and SERVER.EXAMPLE.COM, and consider removing the local file destination if the host’s local disk is small):
@ version : 3.8
options {
chain_hostnames ( no );
create_dirs ( yes );
flush_lines ( 0 );
keep_hostname ( yes );
log_fifo_size ( 256 );
log_msg_size ( 1024 );
stats_freq ( 0 );
flush_lines ( 0 );
use_fqdn ( no );
};
source sys {
internal ();
unix - dgram ( "/dev/log" );
};
source kernel {
file ( "/proc/kmsg" program_override ( "kernel" ));
};
destination messages {
file ( "/mnt/sda1/var/log/messages" );
};
destination SERVER {
syslog ( "SERVER.EXAMPLE.COM" port ( 6514 )
transport ( "tls" )
tls ( ca - dir ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/anchors" )
cert - file ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/logclient.example.com.cert" )
key - file ( "/etc/syslog-ng.d/logclient.example.com.key" )
)
);
};
log {
source ( sys );
source ( kernel );
destination ( messages );
destination ( SERVER );
};
Install the EPEL yum repository: rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm.
Install: yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless mongodb-server pwgen policycoreutils-python.
Start MongoDB: systemctl restart mongod.
Ensure MongoDB starts on reboot: systemctl enable mongod.
Properly label MongoDB’s port: semanage port -a -t mongod_port_t -p tcp 27017.
Install the Elasticsearch yum repository. Add the following to /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo
[elasticsearch-1.7]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 1.7.x packages
baseurl=http://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/1.7/centos
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
Install Elasticsearch: yum install elasticsearch.
Ensure the following settings exist in /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml:
cluster.name: graylog-production
network.host: 127.0.0.1
Start Elasticsearch: systemctl restart elasticsearch.
Ensure Elasticsearch starts on reboot: systemctl enable elasticsearch.
Test Elasticsearch with: curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true; you should see a status of green.
Install the Graylog2 yum repository: rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-1.3-repository-el7_latest.rpm.
Install Graylog2: yum install graylog-server.
Ensure the following settings exist in /etc/graylog/server/server.conf:
password_secret = [random secret generated using: pwgen -N 1 -s 96]
root_password_sha2 = [hashed password generated using: echo -n password | sha256sum]
elasticsearch_shards = 1
elasticsearch_replicas = 1
elasticsearch_cluster_name = graylog-production
elasticsearch_http_enabled = false
elasticsearch_discovery_zen_ping_unicast_hosts = 127.0.0.1:9300
Also consider adding the following:
root_timezone = America/New_York
allow_highlighting = true
Start Graylog2: systemctl restart graylog-server.
Ensure Graylog2 starts on reboot: systemctl enable graylog-server.
Add the following to /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf, repeating variations of the log statement as necessary:
destination d_graylog { syslog("127.0.0.1" port(1514)); };
log { source(s_sys); source(s_net); filter(f_default); destination(d_mesg); destination(d_graylog); };
Properly label the alternate syslog port: semanage port -a -t syslogd_port_t -p tcp 1514.
Install Graylog2: yum install graylog-web.
Ensure the following settings exist in /etc/graylog/web/web.conf:
graylog2_server.uris="http://127.0.0.1:12900"
application.secret="<i>random secret generated using: pwgen -N 1 -s 96</i>"
Start Graylog2’s web frontend: systemctl restart graylog-web.
Ensure Graylog2’s web frontend starts on reboot: systemctl enable graylog-web.
Once Graylog2’s web frontend is running, connect to it (http://localhost:9000/) and configure a log input which matches the syslog-ng configuration. Set the input’s Bind address to 127.0.0.1, its Port to 1514, and also set the its Title .
Permit Graylog web frontend traffic through the server’s firewall:
Place the following in /etc/firewalld/services/graylog-web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<service>
<short>Graylog</short>
<description>Graylog's web frontend</description>
<port protocol="tcp" port="9000"/>
</service>
Run firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service graylog-web.
Download the plugin from https://github.com/Graylog2/graylog-plugin-netflow/releases .
Install the plugin at /usr/share/graylog-server/plugin, ensuring its permissions match the existing plugins.
Reload Graylog and add a NetFlow input using the web frontend.
Permit NetFlow traffic through the server’s firewall:
Place the following in /etc/firewalld/services/netflow.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<service>
<short>NetFlow</short>
<description>Remote NetFlow</description>
<port protocol="udp" port="2055"/>
</service>
Run firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service netflow.